Every year, 13 million Americans are affected by incontinence or involuntary loss of bladder and bowel control. Both men and women, young and old, may experience some form of incontinence that can make them feel ashamed and isolated.
What exactly is incontinence?
- STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE
Stress urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine during laughter, coughing, lifting of objects, or any movement that increases pressure on your bladder. Urine leakage occurs due to weak pelvic floor muscles, poor ligament support at the bladder outlet and urethra, or a defect in the urethral tube itself.
- URGE URINARY INCONTINENCE
Urge urinary incontinence is urine leakage that occurs as soon as you get the urge to go to the bathroom. The sensation is overwhelming, and your bladder muscle contracts (tightens) at the wrong time. You can’t control it.
- OVERFLOW URINARY INCONTINENCE
Overflow urinary incontinence is when the bladder is so full that it leaks urine. The bladder does not empty properly, which leads to continuous leakage. With overflow incontinence, you do not necessarily feel the urge to urinate.
- FUNCTIONAL URINARY INCONTINENCE
Functional urinary incontinence is when your urinary system is normal but you experience leakage because you physically cannot make it to the toilet in time. The amount of leakage may be large.
- FECAL INCONTINENCE
Fecal incontinence is the inability to control your bowels, allowing stool to leak from the rectum. The severity of incontinence may vary from small amounts of stool leaking unexpectedly while passing gas, to complete loss of bowel control.
What causes incontinence?
Many things can contribute to incontinence:
- Bladder infection
- Obesity
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Weak pelvic floor muscles
- Bladder cancer
- Chronic illness/cough
- Constipation/diarrhea
- Damage to the anal sphincter muscles and nerve
- Medications
- Urinary track abnormalities
- Neuromuscular disorders
- Gastrointestinal problems
- Bladder stones
- Stress
- Cigarette smoking
- Caffeine
- Hormonal changes
- Hysterectomy and other surgeries
What you should know about pelvic pain.
More than one third of the American population suffers from some form of chronic pain, and of these, about 50 percent may be partially or totally disabled for a period of days each month. Studies have shown that anywhere from 16 to 33 percent of women experience chronic pelvic pain at some point in their lives. Pelvic pain affects men as well as women.
The pelvic area contains five lumbar vertebrae (backbone), the sacrum (tail bone), the coccyx (tip of tail bone), two pelvic bones, two hip bones, and numerous ligaments, joints, muscles, nerves, and organs, any of which can cause your pain. Pelvic pain can be felt not only in the pelvis, but also in the legs and lower back.

What are common causes of pelvic pain?
Pelvic pain can result from a variety of causes, including:
- Dysfunction of the sacroiliac joint, pubic symphysis, lumbar joints/discs, sacrococcygeal, or hip joints
- Muscle spasm of lower back, hip, pelvic floor, or abdominal regions
- Pelvic organs cramping: uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder, appendix, small and large intestine
- Prolapse of bladder, uterus, urethra, rectum, or small intestine
- Sexually related injuries
- Pelvic inflammation or infection
- Strenuous physical activities
- Bladder stones
- Poor posture
- Nerve impingement
- Gastrointestinal disorders
- Incontinence
- Pelvic Surgery
- Scars and adhesions
- Child-birth injury

Can physical therapy help with incontinence?
There are many ways physical therapy can help you regain control over your bladder and bowels. The focus of a physical therapy program in the treatment of incontinence is improvement of pelvic floor muscle strength. When your pelvic floor muscles are stronger, you have better support for your bladder and pelvic areas and better ability to control bowel and bladder function. Your physical therapist can help you develop a program to address incontinence and pelvic pain, including:
- Exercise – strengthening and training pelvic floor and supportive musculature
- Education on the bladder and normal emptying techniques
- Dietary modifications to avoid bladder/bowel irritants
- Instruction in posture, body mechanics, and bracing the pelvic floor during daily activities
- Biofeedback / Electromyography (EMG) – diagnostic testing that uses electrodes on the skin to record the electrical activity of muscles to help illustrate functional muscle contraction and relaxation
- Manual therapy, including soft tissue and joint mobilization
- Modalities for pain
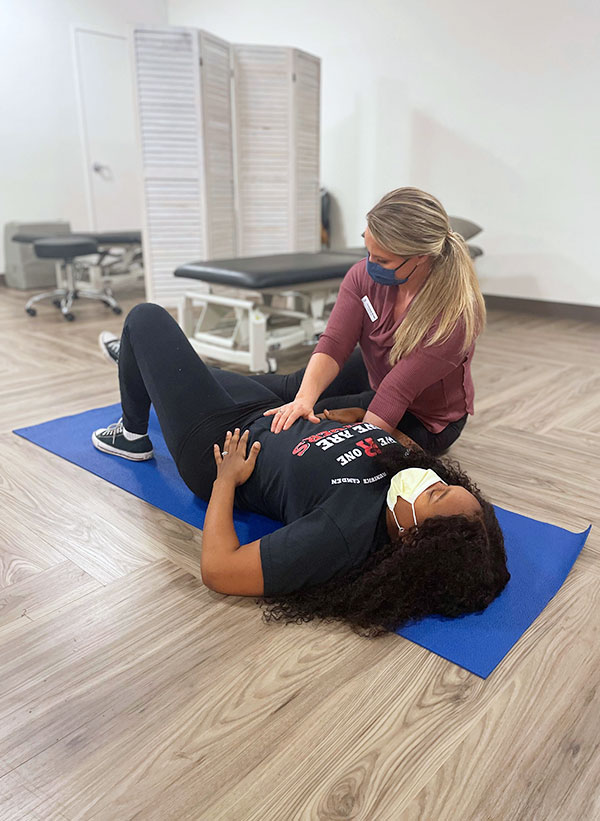


Start your journey to pain-free living today.
Our experts are committed to providing effective, efficient, and compassionate care to help you live a pain-free, active life. Our passion is to help every patient reach their goals on their journey to recovery and optimal performance.



