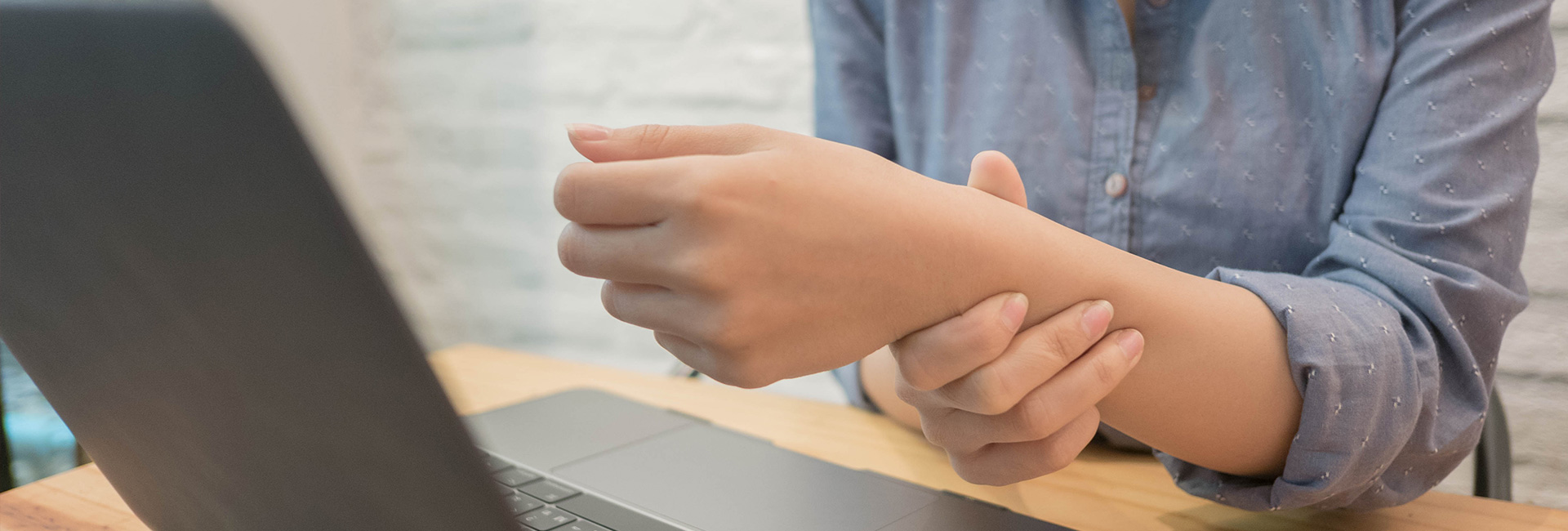
What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that can cause numbness, tingling and sometimes pain and weakness to the hand. These symptoms occur when there is pressure in the wrist on a nerve called the median nerve. The median nerve provides sensation on the palm side of the hand to the thumb, index, and middle fingers, and most of the time to half of the ring finger. The median nerve also supplies the muscles in the palm on the thumb side of the hand. In severe cases you may see muscle atrophy or wasting of these muscles.
Signs of carpal tunnel syndrome
The hallmark symptom of carpal tunnel syndrome is numbness at night and tingling/loss of sensation in the thumb, index, and middle fingers. Common issues with carpal tunnel syndrome include difficulty manipulating small objects, difficulty with holding and gripping items and difficulty with writing and keyboard use.
The carpal tunnel itself if made up of the carpal bones of the wrist and the transverse carpal ligament. The carpal bones form a semi-circle, and the transverse carpal ligament is a very strong ligament that crosses the top of that semi-circle. The medial nerve travels inside this tunnel along with many tendons that allow us to move the wrist and fingers.
Causes of carpal tunnel pain
Carpal tunnel syndrome is associated with activities such as repetitive use, high force gripping, vibration, and continuous use of the hands in extreme wrist range of motion, so it is not necessarily limited to keyboarding/work. Genetic factors can also influence the incidence of carpal tunnel syndrome as can past medical issues such as a wrist fracture.
What if it’s not carpal tunnel syndrome?
Carpal tunnel is often time confused with several other types of upper extremity conditions including cubital tunnel syndrome, De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, cervical radiculopathy, and Reynaud’s disease.
- Cubital tunnel syndrome presents a lot like carpal tunnel syndrome, however there are some differences. Cubital tunnel syndrome is compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow. Symptoms will generally present as numbness of the small and sometimes ring finger of the hand. Generally, there is more numbness at night, hand pain, weak grip, and pain at the inside of the elbow. The main difference is cubital tunnel affects the small finger side of the hand and carpal tunnel affects the thumb and index finger side of the hand.
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is pain that occurs on the thumb side of the wrist at the base of the thumb. It usually presents as pain with use of the thumb or when the hand is moved into ulnar deviation, toward the small finger side of the hand. Numbness is not typically associated with De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, and it usually can be palpated at the base of the thumb.
- Cervical radiculopathy is pain, numbness and possibly weakness that radiates down the upper extremity that is generated from the cervical spine from an irritated nerve root. Numbness from cervical radiculopathy is generally vaguer, and weakness can be traced to muscles served by the specific nerve root that is being affected and symptoms will most likely be present above the wrist.
- Reynaud’s disease causes parts of your body such as your fingers and toes to feel numb and cold in response to cold temperatures. In Raynaud's disease, arteries in the hands and feet will constrict (vasospasm) limiting blood flow to the area. The skin will turn white at first and then can turn blue. As the arteries open and the blood flow returns the skin my burn and tingle and turn more of a purple color. Reynaud’s disease can affect all the fingers where carpal tunnel will primarily affect the thumb, index, and middle finger.
Treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome
If you feel like you may have carpal tunnel syndrome one of the first treatment approaches to relieve symptoms is to wear neutral wrist splints at night. Many people sleep with their wrist flexed for long periods of time at night. This can increase compression at the carpal tunnel causing irritation to the medial nerve. Neutral wrist splints help reduce compression at the carpal tunnel.
Physical therapy can help reduce symptoms of carpal tunnel. Physical therapy for carpal tunnel typically consists of education on ways to reduce stress to the median nerve and upper extremity. Stretching exercises and strengthening activities may be prescribed to restore balance to the wrist and upper extremity. Tendon gliding activities and nerve gliding/flossing may be prescribed to help tissue heal. A physical therapist may visit your workplace to help reduce and modify activities that may be contributing to your symptoms.
If conservative care fails, there are surgical options available for carpal tunnel syndrome. Physical therapy is beneficial following surgery for carpal tunnel in helping the patient with a smooth transition back to full function. This usually entails helping to reduce symptoms, so surgery followed by stretching to regain full range of motion and graded functional strengthening to get you back to all your normal activities.
We look forward to being a part of your healthcare team.
From injury recovery to movement and performance enhancement, patient success is our passion. Our therapists are committed to the application of evidence-based treatment techniques to ensure you experience the best in rehabilitation and preventative care and see progress with every visit.


