Thank you for your question. Without the ability to perform an individualized evaluation of your current condition, we are unable to provide you with a specific diagnosis or recommendations for treatment. However, we can provide you with some general information that we hope is helpful.
In general, several structures can contribute to lateral shoulder pain when moving into external rotation. Some of these structures include muscles in the region, such as the rotator cuff, biceps, and deltoid muscles at the lateral shoulder. Other structures that can contribute include the joints that connect the humerus with the shoulder blade (glenohumeral joint) and the collarbone to the shoulder blade (acromioclavicular joint). Additionally, it’s possible that pain from other body regions can refer pain to the lateral shoulder.
In patients who experience pain with external rotation, it’s common to find areas of weakness or incoordination in the muscles around the shoulder and shoulder blade. In other cases, limited joint motion contributes to the painful external rotation. Flexibility or tightness around the shoulder, back and neck, can also influence movement patterns that may lead to pain. In general, individualized training programs to improve the strength of these muscles tend to help reduce the pain with movement.
Seeking an in-person exam with a physical therapist will help to figure out what may be causing pain in the lateral shoulder. They will be able to design a specific program to help manage the pain and improve the movement of the shoulder that is tailored to the individual’s body and goals. They may use hands-on techniques to guide joint mobility to reduce pain as well as provide exercises to promote pain free movement.
In essence, seeking professional guidance is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of your unique situation and the formulation of an effective plan for pain management and improvement of shoulder function. Physical therapists are adept at crafting individualized solutions that align with your specific needs and goals.
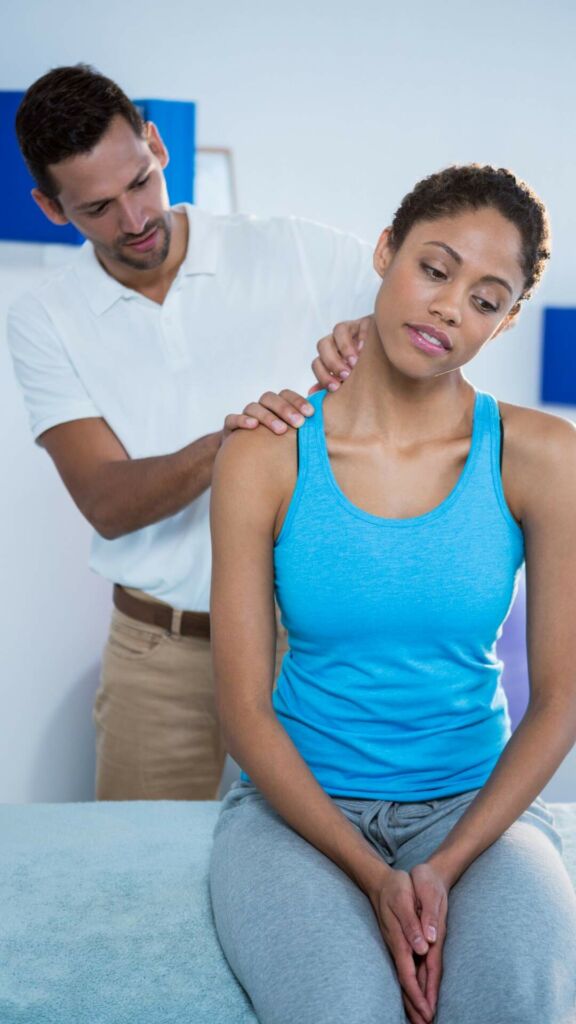

In conclusion, lateral shoulder pain during arm external rotation can stem from various sources, and a holistic approach involving a thorough examination and personalized interventions is essential for effective relief and long-term improvement. Don’t hesitate to consult with a physical therapist to embark on a journey toward a healthier, pain-free shoulder.

Leave pain behind with PT
As physical therapists, we know the importance of movement for overall health and well-being. From injury recovery to achieving optimal performance, our passion is to help every patient reach their goals and live an active, pain-free life.